The majority of business choices made today are informed by data. Companies use data to their advantage for many kinds of daily tasks, from developing new products to acquiring new clients.
They gather information from a variety of sources, including social media, email, cloud mobile applications, and marketing efforts, to name a few.
Businesses struggle to handle the mountains of data existing in their systems since they receive a wide variety of data kinds and quantities on a continual basis.
When organizations exploit the data flood to their advantage and put the proper management systems in place, it can be like magic.
Data Lifecycle Management is one of the most often used strategies that business executives use inside their firms (DLM).
It is a procedure that entails managing data throughout every stage of its lifespan, which starts with the collection and concludes with destruction.
Businesses may use the data as needed by implementing the appropriate DLM techniques.
Let’s examine the three main goals of data lifecycle management that may help you make the most of the data.
But first, let’s discuss what is data lifecycle management in order to grasp that:
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM): What Is It?
An organization’s data management strategy is referred to as data lifecycle management.
Monitoring data at various stages across databases, systems, apps, and storage media is its main goal, regardless of whether you refer to it as a process, collection of processes, or set of rules.
A single piece of data may now do several tasks, thus it is never wasted.
Instead, companies keep these fragments of information in their systems for years in order to connect them with other bits and create a bigger picture.
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) is a never-ending loop as a result of this continuity of data.
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) entails the implementation of rules to control the flow of information in a company’s data systems, including data production, execution, archiving, and everything in between.
Organizations can comprehend, map, and govern their data throughout the journey, as it is generated, published, amended, and stored, thanks to a well-run and robust data management process.
Recommended: Which Statement Describes The Biggest Problem Associated With Technology?
What Are The Three Main Goals Of Data Lifecycle Management (DLM)?
Data management may be challenging for organizations at times. They can monitor and manage the information flow between systems using DLM to maintain it in forms that are useable and accessible.
This is made possible by data lifecycle management’s fundamental aims, which serve as the framework for its simplified and unrestricted data flow.
The following are the Three Main Goals Of Data Lifecycle Management (DLM):
1. Data Security OR Confidentiality
The potential for data abuse is always significant since there is such a vast amount and variety of data accessible for exploitation.
Data security is the top concern of both enterprises and people since it is the engine that powers the commercial world.
Hence, ensuring data security and confidentiality becomes essential.
Data lifecycle management uses data security best practices as one of its key competencies to establish a robust data protection architecture in order to do this.
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) prevents unauthorized users from accessing data (such as cybercriminals). Moreover, it guarantees data security against viruses and corruption.
2. Availability Of Data
In our digital age, data serves as the foundation for many processes, thus it must always be accessible.
Several processes that rely on one another to gather data fail repeatedly when the correct individuals don’t have access to it when they need it. Data-driven services place a high value on data availability.
Hence, DLM provides cloud solutions that make it quickly accessible for clients and staff members before they need it.
3. Data Reliability
Multi-user computer environments are expanding as data-centric technologies gain acceptance. Several copies of the same data may exist when many people simultaneously access the same database.
Data lifecycle management continuously refreshes data in order to prevent redundancy and preserve integrity.
All users now have access to clear and accurate data, enhancing the speed and effectiveness of corporate operations.
Information silos, which may impede crucial company cooperation, are also avoided by DLM.
Recommended: What is Office Technology and Management (OTM), Meaning & All About?
6 Steps Of Data Lifecycle Management
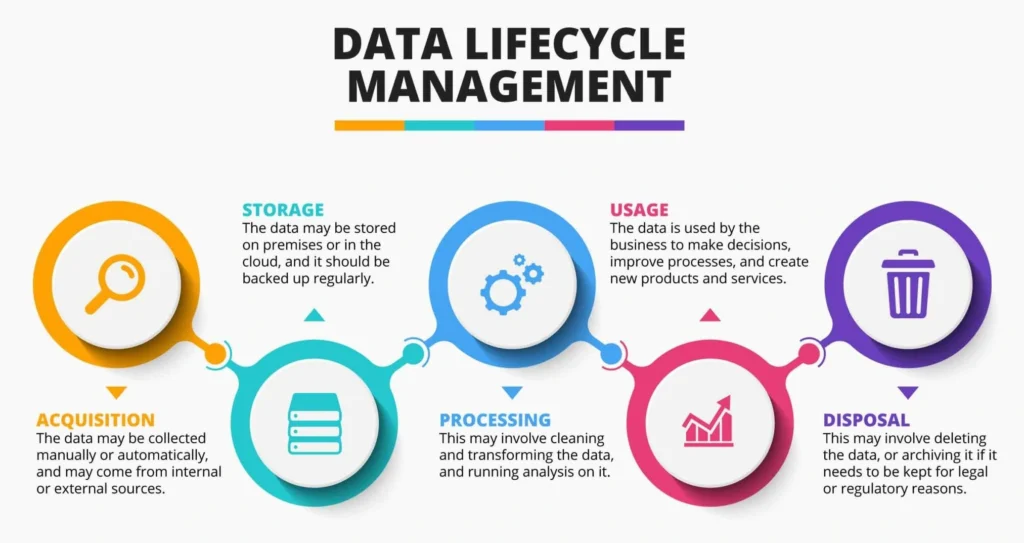
The following six steps are included in the data management lifecycle:
1. Data Gathering
A system receives data either manually or when another system delivers it.
2. Maintaining And Storing Data
After being checked for quality and validity, the data is processed and saved in the appropriate system.
3. Utilization Of Data
The created data is transformed into usable forms that a particular piece of software can comprehend.
4. Publishing Of Data
Data is transferred to the relevant platforms and made available for immediate use (for instance, printed purchase orders with associated data are sent with packages).
5. Data Preservation
The system archives a piece of data after it has served its intended function.
6. Cleansing Of Data
If systems discover that the data is no longer needed, they either clean it up or switch to on-premises or less expensive storage solutions.
These steps represent the passage of information via several business processes.
Continue reading to learn the advantages it may provide you in the form of its objectives.
Recommended: Which Technologies Combine to Make Data a Critical Organizational Asset?
How Can Companies Benefit From Data Lifecycle Management (DLM)?
When it comes to handling the enormous amounts of data they collect and govern, businesses have enormous hurdles.
They provide security oversight and high-quality maintenance of the data they produce using data lifecycle management to achieve a number of benefits.
In order to reduce security risk and manage expenses associated with the construction of large data storage systems, companies may handle a variety of unrelated data safely by using data lifecycle management.
The more advantages that Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) provides include:
- The detection of data bottlenecks.
- Improved historical data handling.
- Enhancing one’s capacity to carry out a root-cause analysis.
- Facilitating data access for teams.
- When data is no longer needed, move it to less expensive on-premise solutions.
In Summary
When implementing data lifecycle management, many businesses make the wise choice to use the appropriate technologies to manage data. DLM enhances several company functions and offers a wide range of benefits.
DLM enables you to manage data as well as avoid silos, and enhance data consistency, dependability, and accessibility across your enterprise systems.
It is now time for your company to put the best DLM strategy into place and control the data flow for all upcoming procedures.
We hope the article on the three main goals of data lifecycle management provided by Multiplextimes.com will be helpful for your business. Thanks!











